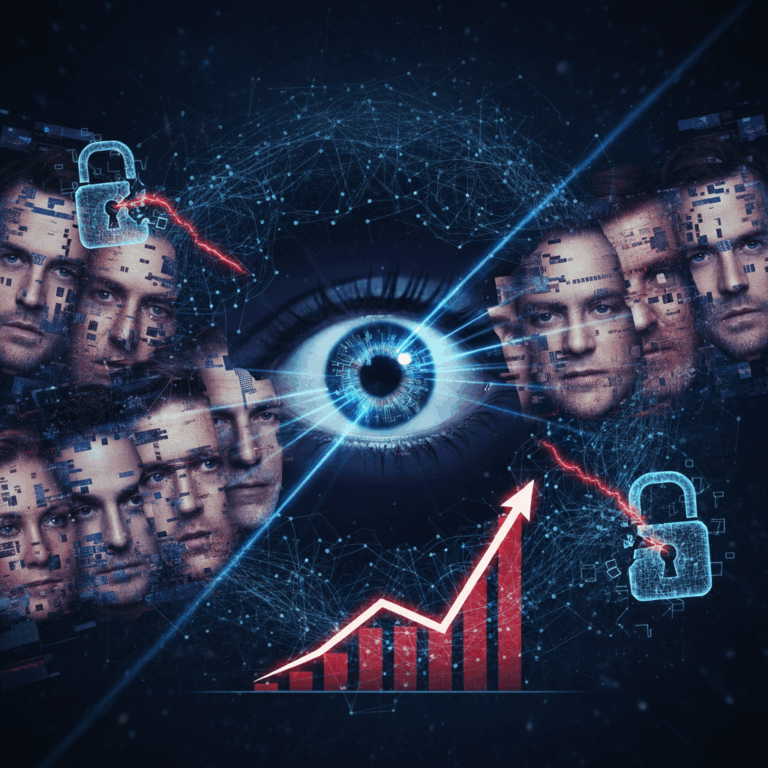
Detecting Deepfakes
The world is facing one of the fastest-evolving digital threats of our time — deepfakes. These AI-generated manipulations of video, audio, and images have reached alarming levels of realism, eroding the line between truth and fabrication. Global cybercrime units have reported a 19% increase in deepfake incidents just within the first quarter of the year, surpassing all cases reported in 2024.
What began as a technological curiosity has now become a weaponized tool for misinformation, identity theft, and financial fraud. Deepfakes are no longer a novelty in internet culture — they’re a fundamental cybersecurity concern with far-reaching implications for individuals, corporations, and governments alike.
What Exactly Are Deepfakes?
The term deepfake comes from deep learning and fake. It refers to synthetic media generated by artificial intelligence that convincingly replaces a person’s face, voice, or movements with those of someone else.
At the core of deepfake creation lie Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) — AI systems where two neural networks compete: one generates fake content, and the other tries to detect it. Through this iterative process, the AI improves its output until the fake becomes virtually indistinguishable from reality.
Modern deepfakes can now replicate subtle facial gestures, blinking patterns, and speech intonation with uncanny accuracy. As a result, it’s possible to fabricate videos of politicians making false statements, executives authorizing fake transactions, or celebrities involved in fabricated scandals.
The Explosive Growth of Deepfakes
According to reports from the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) and Cyber Threat Alliance, deepfake-related threats have grown over 40% between 2023 and 2025. The global distribution of these attacks shows notable spikes in the United States, India, Europe, and Latin America — regions with heavy digital infrastructure and active social media ecosystems.
Deepfakes are now used for:
- Corporate fraud: impersonating executives to authorize bank transfers.
- Political manipulation: spreading false statements during election campaigns.
- Blackmail and extortion: creating fake compromising videos.
- Bypassing biometric security: tricking facial recognition systems.
In early 2025, an alarming case in Hong Kong involved a forged video call where fraudsters posed as a company CFO to authorize a $25 million transfer — all through deepfake video conferencing. The criminals succeeded by exploiting the trust factor inherent in visual communication.
Vastav AI: India’s Technological Defense Against Deepfakes
To counter this escalating threat, developers are building advanced AI-driven detection systems. Among the most promising innovations is Vastav AI, an Indian-developed platform designed to identify deepfake content with over 94% accuracy.
Vastav AI’s detection model uses a multi-layered analysis pipeline, which includes:
- Lighting and shadow inconsistencies: Analyzing physical light behavior that doesn’t match real-world physics.
- Facial micro-movements: Detecting unnatural blinking, lip synchronization, and subtle muscular distortions.
- Audio spectral fingerprinting: Identifying tonal patterns or harmonics that deviate from genuine human voices.
- Metadata and compression pattern analysis: Revealing hidden signs of editing or rendering.
Unlike conventional systems, Vastav AI continuously trains on massive datasets of real and synthetic content, allowing it to evolve alongside emerging deepfake creation techniques.
This approach makes it a powerful tool not only for cybersecurity firms but also for media companies, banks, and government institutions that need to verify digital content integrity in real time.
The Paradox: AI as Both the Weapon and the Shield
Ironically, the same technology that empowers deepfake creation is also the best hope for their detection. Modern artificial intelligence is being developed to fight back against its own misuse.
Advanced AI systems can now evaluate pixel-level anomalies, analyze voice cadence, and even assess the emotional authenticity behind speech patterns. Researchers are also exploring “AI watermarking” — hidden digital signatures embedded during the content generation process, enabling traceability and authentication later.
Major AI research labs, including OpenAI, Google DeepMind, and Anthropic, are collaborating with cybersecurity organizations to design AI verification standards that allow cross-platform identification of manipulated media.
The Real-World Consequences
The rise of deepfakes has created a new era of digital distrust. The damage extends far beyond individual victims:
- Political Instability: Fake videos of world leaders can trigger real diplomatic crises.
- Corporate Fraud: Forged executive communications have already cost companies millions.
- Personal Reputational Damage: Victims of non-consensual fake pornography face long-term psychological harm.
- Judicial Challenges: Courts struggle to determine the authenticity of digital evidence.
- Biometric Vulnerability: Deepfake audio and video can bypass voice and facial recognition systems.
This new digital battlefield threatens the very fabric of truth in the information age. The ability to believe what we see — once a cornerstone of communication — can no longer be taken for granted.
Global Regulation and Policy Efforts
Governments around the world are scrambling to legislate deepfake technology before it spirals out of control:
- United States: Lawmakers propose federal criminal penalties for malicious deepfake distribution.
- European Union: The AI Act 2025 enforces transparency labeling for AI-generated media.
- India and South Korea: National platforms for real-time audiovisual verification are under development.
- Latin America: Countries such as Mexico, Chile, and Peru are forming partnerships with the private sector to monitor misinformation campaigns.
However, regulation still lags behind innovation. The rate at which deepfake technology evolves outpaces legal and ethical frameworks, creating a dangerous regulatory vacuum.
Strategies for Defense and Awareness
Defending against deepfakes requires a multifaceted strategy that combines technology, education, and international collaboration.
- Public awareness: Teach individuals how to recognize signs of synthetic media.
- Verification tools: Encourage use of AI-based detectors such as Vastav AI or Deepware Scanner.
- Cross-referencing sources: Verify authenticity before sharing or reacting to viral content.
- Secure metadata tracking: Embed verifiable digital fingerprints in all media files.
- Industry collaboration: Create shared databases of detected forgeries to enhance AI training accuracy.
Organizations like the Content Authenticity Initiative (Adobe) and Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) are already developing open standards for traceable digital content verification.
AI’s New Frontier: Authenticity as a Service
The future of cybersecurity may lie in “Authenticity as a Service” (AaaS) — platforms that automatically certify, track, and verify every digital asset uploaded to the internet.
Emerging solutions integrate blockchain technology with AI authenticity scoring, ensuring that every piece of media carries an immutable signature of origin. This technology could revolutionize journalism, social networks, and even law enforcement by creating tamper-proof digital ecosystems.
Meanwhile, AI developers are working on provenance engines — software capable of analyzing billions of data points to determine whether an image or video was generated, edited, or captured by a real device.
Deepfake Detection in Biometric Security
One of the most alarming implications of deepfakes is their potential to bypass biometric authentication. Cybercriminals have begun using synthetic voices and facial animations to access restricted systems or impersonate users.
To combat this, cybersecurity firms are now embedding deepfake-resistant biometric protocols that include:
- Liveness detection: Ensuring the subject is physically present during authentication.
- Motion pattern analysis: Studying natural head and eye movement inconsistencies.
- 3D depth mapping: Identifying flat, generated surfaces masquerading as real faces.
These innovations are critical for securing financial systems, government databases, and personal identity management in a world where visual truth is no longer guaranteed.
Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
As technology evolves, it’s clear that human judgment remains irreplaceable. While AI can detect deepfakes with increasing accuracy, final validation often requires human expertise — analysts capable of interpreting contextual cues, linguistic nuances, or metadata inconsistencies.
The most successful defense model will be hybrid: artificial intelligence conducting large-scale automated scanning, combined with human oversight for high-risk cases.
Educational initiatives are also vital. Universities and cybersecurity institutions worldwide are now introducing deepfake literacy programs, teaching students and professionals how to recognize manipulation signals and maintain digital integrity.
The Psychological Impact of Deepfakes
Beyond the technical and legal consequences, deepfakes are reshaping the psychological landscape of digital trust. Victims of deepfake attacks often report anxiety, paranoia, and loss of reputation, while audiences grow increasingly skeptical of authentic content.
This collective skepticism can lead to the liar’s dividend — a phenomenon where genuine evidence is dismissed as fake simply because deepfakes exist. In this sense, the technology not only fabricates lies but also destroys the credibility of truth itself.
Future Outlook: Toward a Safer Digital Reality
The battle against deepfakes is ongoing, but not hopeless. The next five years will likely see a rise in:
- AI-certified journalism: Every visual verified by authenticity algorithms.
- Government verification APIs: Automatic screening of media before publication.
- Consumer-grade authenticity checkers: Built into smartphones and social media apps.
- Ethical AI frameworks: Mandatory disclosure for all generative media.
Society is moving toward a new era of digital authenticity, where transparency and verification are not optional but fundamental to maintaining democracy, security, and human dignity online.